Motivation
The edgesec tool implements a set of algorithms for edge-based routers addressing fundamental security weaknesses that impact current IP and IoT router implementations.
Why?
Most internet gateways, (indeed most IP addressable device on an internal network) have a fundamental weakness: they are not well secured. Recent research by Symantec shows that 75% of reported attacks on IOT devices were due to router weaknesses.
Security assumes if you have access to the network you are trusted. This is clearly a mistaken assumption.
Edge routers, internal networks and more advanced IoT networking need fundamental innovation to address the security weakness. New architectures are needed for UI bootstrapping, key distribution, key storage, network segmentation, service discovery and addressing that will work as well at the edge as it does on the open internet.
Ambition
The edgesec toolset provides the following solutions to solve the main IoT gateway security challenges:
- A mechanism to do network isolation at the router/gateway level. This network isolation will protect against external and internal entities attacking connected IoT devices.
- A discovery mechanism for the gateway and IoT devices.
- A mechanism to store encryption keys and confidential router data.
- A mechanism to monitor connected IoT devices at the router level. By defining the minimal data collection standards, we have in place a powerful technique that will assist with the early detection and later containment of security threats coming from compromised IoT devices.
We integrate all of the above strategies into a single opensource codebase that lays the foundation for a secure IoT gateway and will be used as a standard for IoT device connectivity.
Technical approach
Network Management
Network Management techniques are implemented at the WiFi level protocol. We are using the VLAN mechanism to segment the network of connected devices. We are considering two types of isolation: internal and external. The internal isolation is based on subnets as depicted in the example picture below:
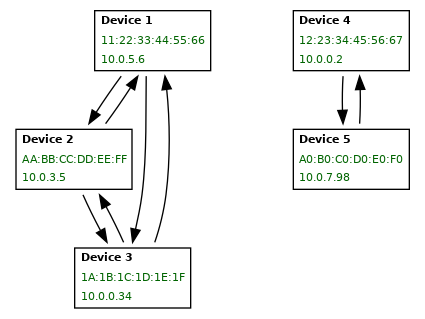
There are five devices located in five separated subnets. The arrows indicate the bridge connection between devices. Note that device 1 can not communicate with devices 4 and 5, and vice-versa.
The external isolation is based on denying a particular device access to the external network. An example is provided in the below figure:
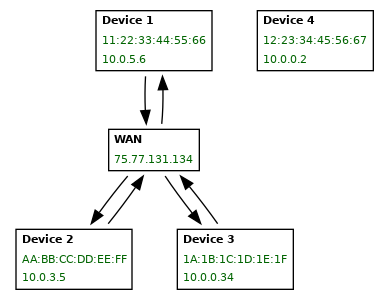
Here devices 1, 2 and 3 can access the external network. However device 4 has no access.
Traffic monitoring
Network Capture is implemented with traffic capture libraries and middlewares that allows storing the captured metadata in SQLite databases and pcap files.
Device discovery
The Device Discovery procedure makes sure that the connected devices can find themselves across subnets. At the core of the discovery procedure, is the ability to monitor and forward the mDNS traffic emanating from the connected devices.
Secure storage
The Secure Storage module stores the encryption and signing keys, and router confidential data into a generic key value store, which can be encrypted using the hardware secure element of the router (if available).
The functionalities of all of the above modules can be accessed using the supervisor API.